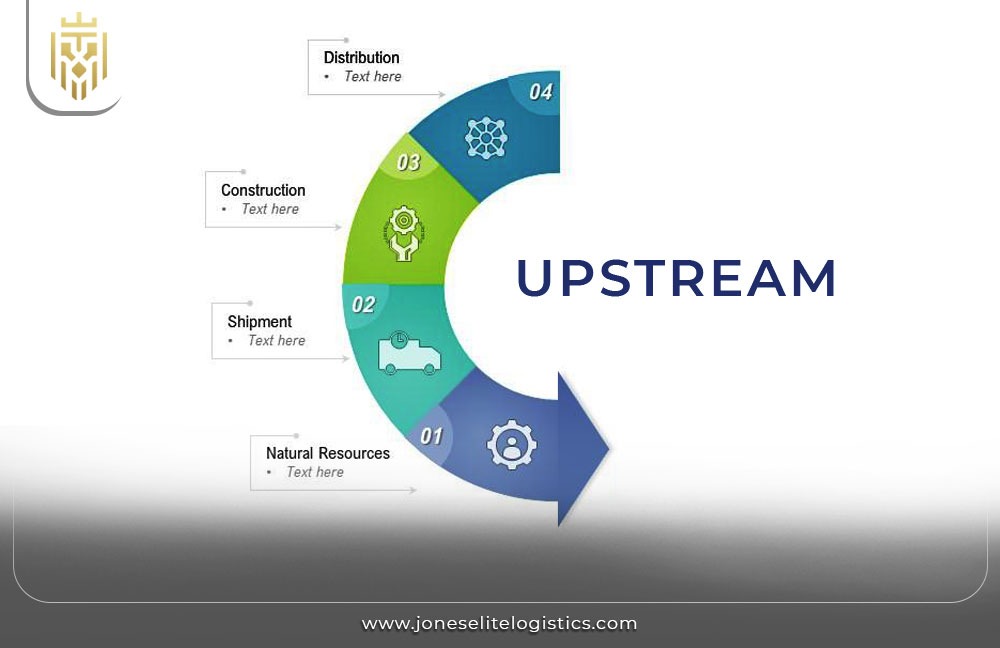
What is an Upstream Supply Chain?
The upstream supply chain refers to the part of the supply chain responsible for the sourcing of raw materials and transporting them to manufacturers. In this phase, companies focus on securing the essential components needed for production from various suppliers.
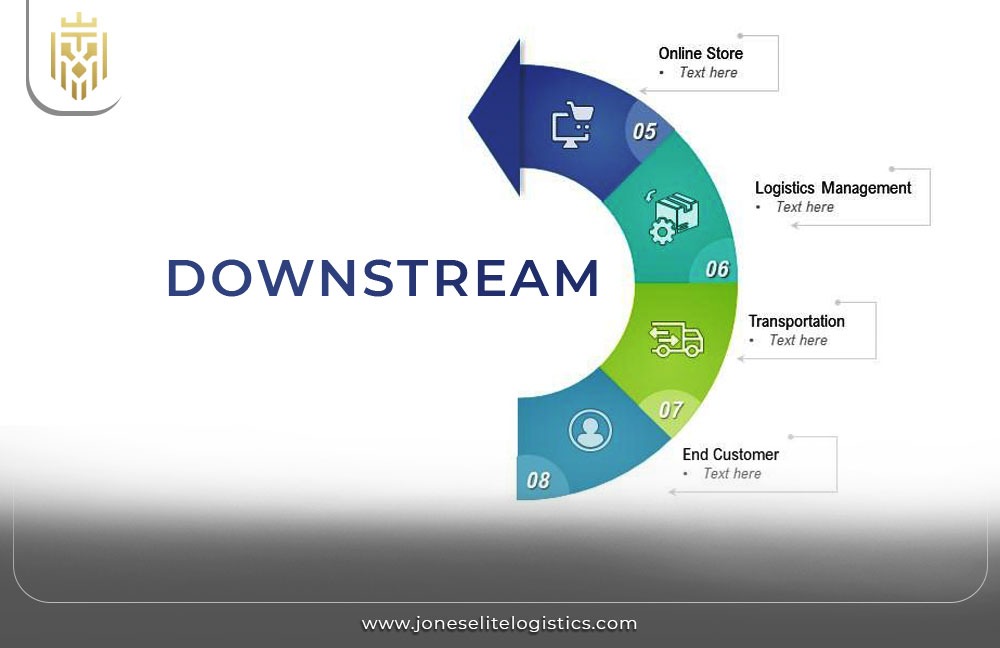
What is a Downstream Supply Chain?
The downstream supply chain is the process of delivering the finished products from manufacturers to the end customer. It involves managing distribution channels, logistics, and customer service to ensure that the product reaches its final destination efficiently.
Difference between Upstream and Downstream Supply Chain:
The upstream supply chain focuses primarily on the flow of raw materials, ensuring that the production process has the necessary inputs. On the other hand, the downstream supply chain prioritizes the flow of information and the efficient distribution of finished products to meet customer demands.
Challenges in the Upstream Supply Chain:
Significant challenges, such as port congestion, disruptions like labour strikes and fluctuating raw material prices in the global supply chain, and managing the risks associated with fluctuating market demands are generally the problems faced in supply chain upstream. Additionally, there is an increasing focus on sustainability and inventory management to ensure long-term viability.
Challenges in the Downstream Supply Chain:
The downstream supply chain is often strained by rising freight costs, the pressure to meet tight delivery deadlines, and the constant need to adapt to shifts in customer preferences. These challenges make it critical for companies to maintain flexible operations to satisfy market demands.

How can Upstream and Downstream Supply Chains be managed effectively?
Both supply chains can be effectively managed by ensuring a smooth flow of key resources materials, money, and information between them. This leads to increased efficiency and reduced operational costs.
Flow of Materials:
Effective management of the flow of materials is crucial, involving careful procurement of raw materials, components, or finished goods, managing transportation logistics and supplier relationships. Efficient supply chain management practices ensure that these flows are well-coordinated and maintained, ensuring a consistent supply of raw materials and inputs, keeping production timelines intact.
Flow Of Money:
Money flows through the supply chain as customers make payments for products, and businesses pay distributors and suppliers. In times of economic downturn, companies must adjust their financial strategies to maintain balance across both upstream and downstream activities.
Flow Of Information:
Maintaining a consistent flow of information between upstream and downstream teams ensures trust, transparency, and collaboration between everyone involved. Proper supply chain management ensures that information flows are optimized, reducing the risk of miscommunication. Regular communication helps anticipate supply chain disruptions and provides clarity, aiding both production and distribution efficiency.
FAQs
1) How is the Upstream Supply Chain explained?
The upstream supply chain refers to the part of the supply chain responsible for the sourcing of raw materials and transporting them to manufacturers. In this phase, companies focus on securing the essential components needed for production from various suppliers.
2) How is the Downstream Supply Chain explained?
The downstream supply chain is the process of delivering the finished products from manufacturers to the end customer. It involves managing distribution channels, logistics, and customer service to ensure that the product reaches its final destination efficiently.
3) What is the Difference between Upstream and Downstream Supply?
The upstream supply chain focuses primarily on the flow of raw materials, ensuring that the production process has the necessary inputs. On the other hand, the downstream supply chain prioritizes the flow of information and the efficient distribution of finished goods to meet customer demands.
4) What are the Challenges in the Upstream Supply Chain?
Upstream supply chains face significant challenges, such as port congestion, disruptions in the global supply chain, and managing the risks associated with fluctuating market demands. Additionally, there is an increasing focus on sustainability and inventory management to ensure long-term viability.
5) What are the Challenges in the Downstream Supply Chain?
The downstream supply chain is often strained by rising freight costs, the pressure to meet tight delivery deadlines, and the constant need to adapt to shifts in customer preferences. These challenges make it critical for companies to maintain flexible operations to satisfy market demands.