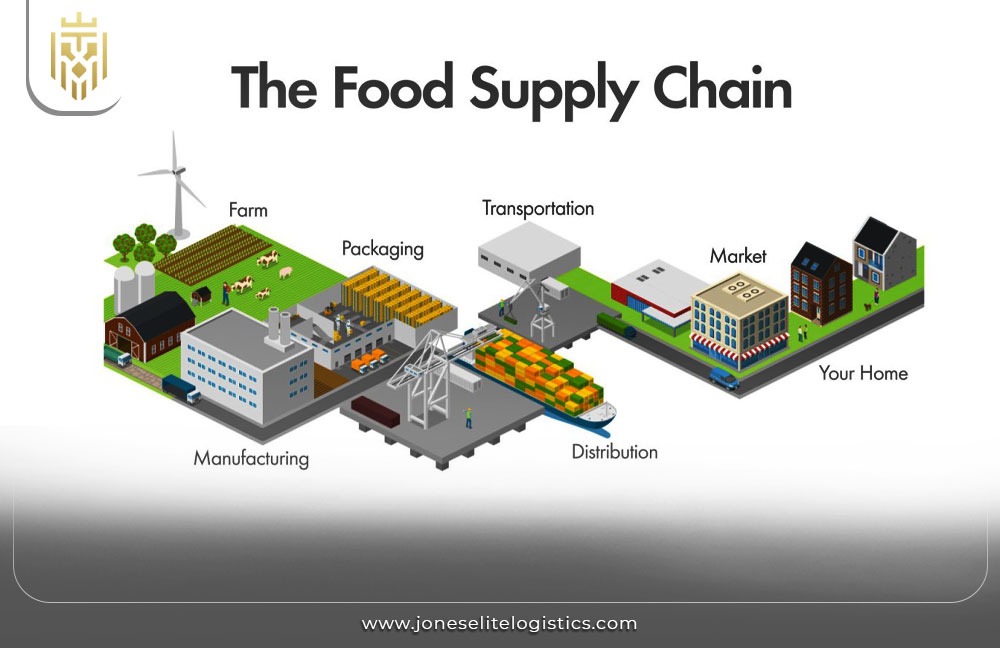
What is the Food Supply Chain?
The food chain refers to the food system and pathways through which food items are produced, processed, preserved, marketed, and utilized. There is production of agricultural raw materials, processing and packaging of the raw materials, transportation of the final product, and retail selling and consumption by the end user. This chain helps in getting food products from the farm to the table with the help of food processors while at the same time observing quality and safety measures.

Importance of Food Supply Chain in India:
The necessity for India to efficiently manage the food supply chain arises with an emphasis on food security, minimizing wastage, and quality nutrition. Due to such a large population base and the geographical nature of the country, the effective supply chain allows for better distribution and allocation of food to all regions; the improvement benefits farmers and overall food manufacturers and satisfies the increasing demands for different kinds of food products hence slowing the rate of increasing food prices which have economic impacts.
How it Works:
The food supply chain works through a series of interconnected steps: production, processing packaging, transfer, distribution, and utilization. All the stages have many players such as farmers, processors, transporters, retailers, and consumers. Thus, efficient coordination and administration of these stages is paramount to ensure quality, safety, and timely delivery of food items thereby reducing wastage.
Difference between Regular Supply chain and Food supply chain:
Two primary events that the food supply chain also features are different from a general supply chain: they are based on the type of products, namely, food. Foods are heat sensitive, which makes their handling, storage, and transportation conditions to be very critical. The food supply chain entails factors like spoilage, food temperatures, and compliance with the food laws and regulations which are not very relevant in a normal supply chain of other products.
Steps in the Food Supply Chain:
The food supply chain comprises several steps: such processes as production, handling and storage, processing, packaging, transportation and distribution, retail, and finally consumption. Each of them consists of certain activities and control measures so that the food products can be maintained in proper conditions of safety, quality, and edibility. Optimal implementation of these steps decreases the wastage, cost, and delivery time to the consumers.
Production:
Farming is an example of production which is the first process in the food supply chain since it involves the growing of food. This stage comprises activities like farming involving crop production, growing crops for food, feeding, and rearing of animals for food production such as; meat and dairy products. It is squeaky clean that sustainable practices and modern technology are useful in increasing productivity, improving the quality of products, and minimizing environmental issues.
Handling and Storage of Food Products:
Pesticides and other chemicals or residue on fruits and vegetables mean that handling and storage of the food products are very important. At this stage, cleaning and packaging, grading, and storing under specific environmental conditions that will not influence spoilage and contamination. Adequate cool storage structures and other storehouses are very essential requirements for storing such perishable foods as fruits, vegetables, dairy, and meats among other foods to get to the consumer in their best form.

Distribution:
Distribution refers to the conveying of food products from producers and warehouses to the planned centers of consumption including wholesalers, retailers, and food service organizations. The efficient management of the supply chain requires an efficient transport system to be able to transport the produce to markets or consumers within the stipulated time with the right temperature and cleanliness that do not allow bacteria to grow on the produce.
Consumption:
Consumption is the last level in the food supply chain whereby the final consumers acquire and utilize foods. This stage emphasizes that food products must be safe, healthy, and of superior quality from the time they are produced to the time they are consumed. Information collected from consumers can inform changes in the operation of the supply line whereby the ways of producing, handling, and distributing goods and services are altered to fit consumer preferences.
Types of Food Supply Chain:
Existing food supply chains differ based on food supply chain requirements that meet particular product types. Some of the classifications include continuous flow supply chain, efficient supply chain, custom configured supply chain, agile supply chain, and flexible supply chain. They consist of different sub types that have unique characteristics oriented to provide the best conditions, movement, and quality of the food products, to provide to the consumers.
Continuous Flow:
A continuous flow supply chain is best suited for the products that get used up quickly, and are reputed to be constant sellers, such as grains and dairy products. Common and uninterrupted rhythms of production and delivery are spoken of as the key forms of its operation. This type is suitable for products with a relatively stable demand that also guarantees products’ timely availability and food quality.
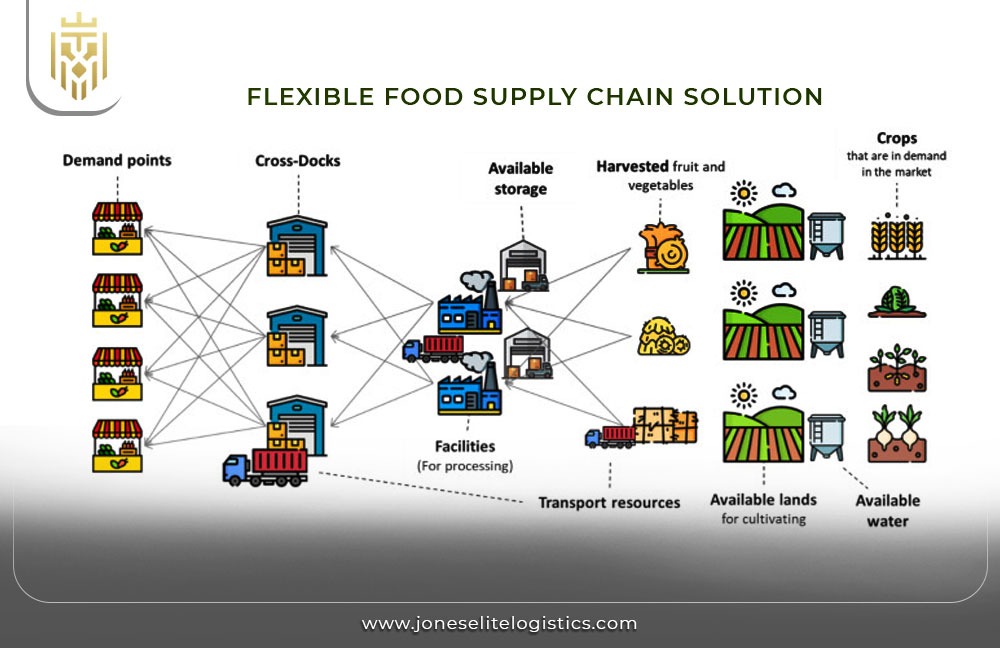
Efficient:
Lean supply chain management involves cost reduction and the elimination of the unnecessary in delivering products to the consumer. It is mirroring most tailor-made with non-perishable and low-variability food products. This type ensures that a wide range of products such as staple foods and other basic commodities are supplied most efficiently and cheaply by alleviating key factors such as resource optimization, inventory dimensioning, and logistics.
Custom configured:
A configured supply chain is where an organization has made particular adjustments and modifications to suit the requirements of a few products or markets. It also contains the features of other supply chain types to accommodate special requirements such as seminar products or small specialty markets. This flexibility enables effectiveness in handling, storage, and distribution of any particular food items that are variant in quality and market availability.
Agile:
An agile supply chain is also characterized by the ability to make changes very quickly because of fluctuating markets and risks inherent in the marketplace. They are suitable for perishable and high variability items, that is, goods that have short shelf life. It is mostly characterized by a fast rate of flow, volatility, and flexibility that enables fast switching of operations according to the changes in consumers’ preferences and even seasons.
Flexible:
A flexible supply chain solution can be used with various types of products and demand characteristics. It is more of a middle ground between efficiency and agility, thus it can be used on most food products. This type of supply chain can always respond positively towards change so that both regular and sources of uncertainty are fulfilled in a way that achieves the right balance between cost and flexibility.
Challenges of Food Supply Chain Management:
There are so many factors affecting the management of the food supply chain in India such as the challenge of food safety, supply chain disruptions, high cost of maintenance, and sustainability challenges among others. These issues entail teamwork and creativity to sustain the reliability, promptness, and robustness of the supply chain.
Food Safety :
The challenge that is central to the restaurant business is the sanitation of foods since most of them are perishable. In this case, one must ensure cleanliness to avoid the spread of diseases, avoid polluting the environment, and practice safety measures to reduce the incidence of disease. Incidentally, proper storage and transportation conditions are important in maintaining the quality of the food products as it gets to the consumer from the production point.
Supply Chain Disruptions:
Fluctuations in the supply chain like calamities, political unrest, or some other functional complications affect the supply and distribution of food products. They result in time losses, high costs, and food waste. This is why organizations should create sound contingency policies, upgrade the facilities where business takes place, and focus on better efficient communication during an interruption.
High Supply Chain Maintenance Cost:
It covers costs which include transport costs, storage and handling costs, as well as costs of meeting food safety requirements. These costs include; Such costs can be demanding on the available resources, particularly to smallholder farmers and producers. Some of these expenses can be managed and reduced by incorporating new technologies and improving the system of distribution and flow of products in the organization.

Sustainability:
Sustainability must become a focus for the food supply chain since this plays a great role in fueling environmental problems. This entails environmentally friendly farming, optimal use of raw materials, and minimal emissions from the use of vehicles in the movement of food and other products. Promote the use of Non-conventional energy, Eco-friendly packing, and proper disposal of wastes.
FAQs
1) What is the Food Supply Chain?
The food chain includes the actual processing and distribution of fresh food items from the producer, packer, transporter, and consumer point of view. It makes sure that food products reach the end consumers safely and in the shortest time possible.
2) What is the difference between a Regular Supply Chain and a Food supply chain?
A food supply chain deals with perishable goods, which need to be moved within a certain temperature range as well as maintain a higher level of hygiene than the general supply chain for nonperishable items. This increases the food supply chain vulnerability and length of the chain.
3) What are the benefits of Types of Food Supply Chain?
Depending on the supply chain type which might be efficient or agile the benefits are the evaluation of cost, flexibility to meet demand, and minimized utilization of resources. They cater to all the product needs hence improving on quality and supply.
4) What are the challenges of Food Supply Chain Management?
Some difficulties are the ability to provide hygiene, instability, high expense, and ecological impact. Solving these problems involves proper approaches and openings in the aspect of technology and structures.