Introduction to Supply Chain Management and its Functions:
Supply Chain Management (SCM) refers to the integration of sourcing, manufacturing, storing, and distributing functions into streamlined operations to optimize customer satisfaction. It ensures cost-effective and smooth product movement through improved coordination of various processes. Understanding the functions of supply chain management are procurement, production, and logistics, helps businesses improve performance and meet market demands effectively.
Objectives of Supply Chain Management:
The key objectives of supply chain management include cost reduction, quality control, enhanced visibility, agility, and customer satisfaction. This area may involve proper procurement, production, and distribution and optimising inventory levels, minimising risk, and being responsive to market demands.
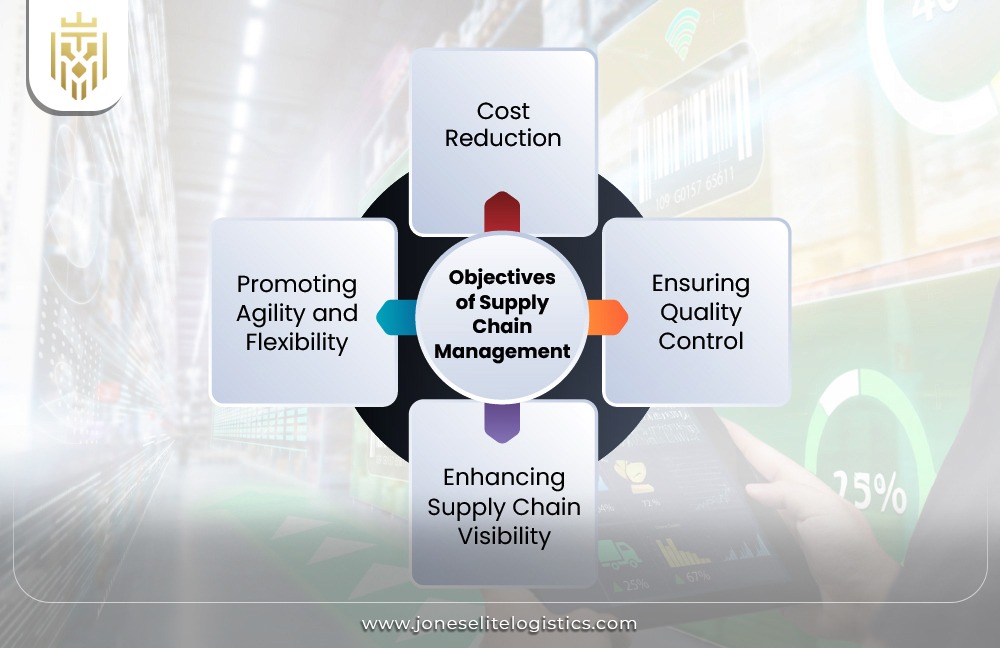
Cost Reduction:
The reduction of costs for supply chain management involves optimization in procurement, transportation, inventory, and distribution to save money. Cost-effective practices could help the businesses boost profits while keeping competition at bay. This helps to ensure financial efficiency while maintaining high service standards across the 3 functions of supply chain management.
Ensuring Quality Control:
Maintaining product quality compliance with standards and customer expectations is an important part of supply chain management. Rigorous inspections and collaboration with suppliers help shield against defects that might taint the reputation of brands. From all supply chain functions, quality control is that which guarantees consistent superiority of products, from raw materials to final consumers.
Enhancing Supply Chain Visibility:
Supply chain management improves visibility through real-time tracking of goods; thereby assisting better decision making and inventory control. Increased transparency reduces risk and enhances efficiency, leading to a better customer experience. A well-managed supply chain functions well when visibility is an integral priority of all stages of operation.
Promoting Agility and Flexibility:
Agility and flexibility in supply chain management enable organizations to respond well to changes in the market or disruption of operations. Resources and production are rapidly adjusted to a level where rapid adaptability comes into play. The 3 functions of supply chain management benefit from flexibility enhancement, giving companies a competitive edge in changing environments.
What are the Key Functions of The Supply Chain Management?
The seven key functions of supply chain management are procurement, purchasing, production, logistics, warehousing and distribution, information workflow, and customer relationship management. These functions ensure that everything runs smoothly, at the lowest cost without compromising on quality, and ensures the customer receives the product from the suppliers seamlessly.
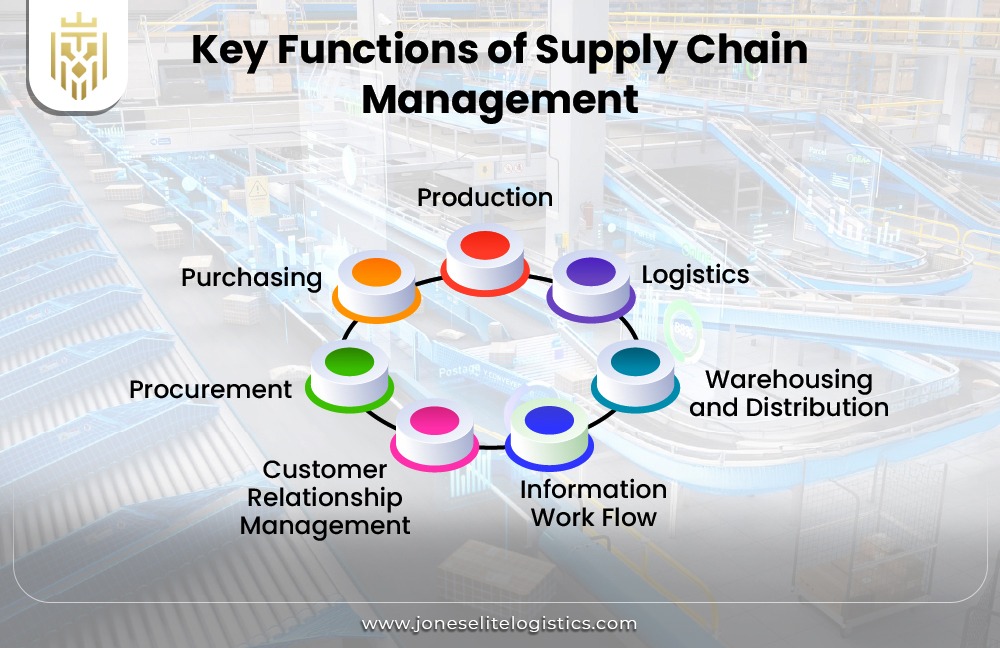
Procurement:
Procurement, a key supply chain function, involves sourcing material, negotiating contracts, and managing relationships with suppliers. It is about cost control, strategic sourcing as well as risk management all to ensure a reliable supply chain. Knowledge of the functions of supply chain management will enhance the procurement process in the business.
Purchasing:
Purchasing is a vital operation within supply chain management, for example, selecting suppliers, negotiating deals, and obtaining materials for production. Timely procurement secures a manufacturing process that is efficient and cost-effective.
Production:
Production management within supply chain management involves the planning, sourcing, inventory, and quality management roles. Efficient handling of resources results in timely product delivery and savings on costs. It is one of the vital supply chain functions that impacts directly business efficiency as well as customer satisfaction.
Logistics:
Under supply chain management logistics, efficient movement of goods through warehousing, order fulfilment, and transportation will capture the essence of proper demand forecasting for effective inventory management. As for what the functions of supply chain management are, logistics smoothens both internal and external processes of an organization.
Warehousing and Distribution:
Warehousing and Distribution are the two most vital supply chain functions responsible for storing, fulfilling orders, and dispatching inventory on time. All of these stock management contributes to how effective inventories can be held to avoid stock shortages as well as the overall efficiency of the supply chain. Thus, these processes reply to function the supply chain performs.
Information Work Flow:
Agile information flow in supply chain management ensures the seamless communication between suppliers, manufacturers, and customers. It eases organization by using real-time data sharing across the enterprises to enhance decision-making and execution within operations. Enriching supply chain functionality with efficient data management helps in overall optimization of the supply network.
Customer Relationship Management:
Customer Relationship Management (CRM), when applied in supply chain management, gives alignment between production and distribution to market demand. It helps businesses in drawing customers so that they can improve their sales and benefit from high customer satisfaction.
FAQs
1.What are the objectives of supply chain management?
The key objectives of supply chain management include cost reduction, quality control, enhanced visibility, agility, and customer satisfaction. This area may involve proper procurement, production, and distribution and optimising inventory levels, minimising risk, and being responsive to market demands.
2.What are the 7 key functions of supply chain management?
The seven key functions of supply chain management are procurement, purchasing, production, logistics, warehousing and distribution, information workflow, and customer relationship management.
3.What are the 3 functions of supply chain management?
Essentially, over the entire process of supply chain management, three basic functions can be identified: procurement, production, and logistics. Procurement secures materials, production transforms them into goods, and logistics ensures efficient storage and distribution, optimising costs, quality, and delivery to meet customer demands.







