Overview of Reverse Logistics:
The phenomenon of reverse logistics refers to the means by which product returns and other goods delivered to a particular place are transported back to the manufacturer or distributor to be returned to the supplier for possible repair, recycling, or disposal. Unlike forward logistics, which focuses on the flow of products from manufacturers to end users, reverse logistics deals with the flow of a returned item from consumers back to manufacturers, emphasizing sustainability and recycling.
What is Reverse Logistics:
Reverse logistics is the process that involves returns, after the use of the products or receipt of equipment and materials by the consumer or end user. This entails receiving returned products that the buyer no longer wants, repairing or reconditioning them, or managing returns effectively. This goal is to achieve maximum return on the total amount of assets, contributing to a circular economy, and at the same time reduce wastage and a step towards sustainable supply chain management.

Importance of Reverse Logistics:
Effective reverse logistics helps in implementing returns processes, enabling customers to receive value while creating less waste. It ensures a business complies with environmental regulations and enhances the company’s image. It aids sustainable development, ensures the company’s conformities to environmental laws, and aids in the recovery of value from returned inventory.
What are the 5 Rs of Reverse Logistics?
The 5 R’s—Returns, Resale, Repair, Repackaging, and Recycling—are critical in managing returns. Each asset step encompasses various approaches in managing returned items, realizing value, and minimizing environmental effects.
Returns:
Returns refer to taking back products from customers dissatisfied due to defects or other factors. Effective reverse logistics processes are critical to customer relations and logistics in order to evaluate and perform a proper disposal of returned goods.
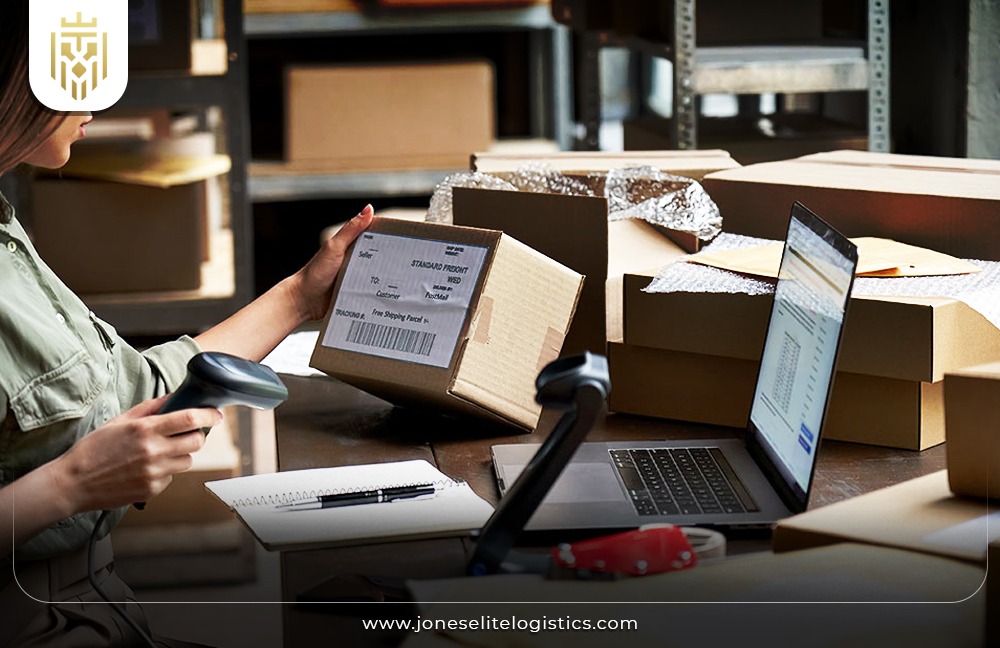

Reselling:
Reselling involves processing returned products, including cleaning or repairing, to return them to the market. Reselling returns a value on goods returned by customers minimizes the amount of waste, and offers affordable, refurbished items back to them.
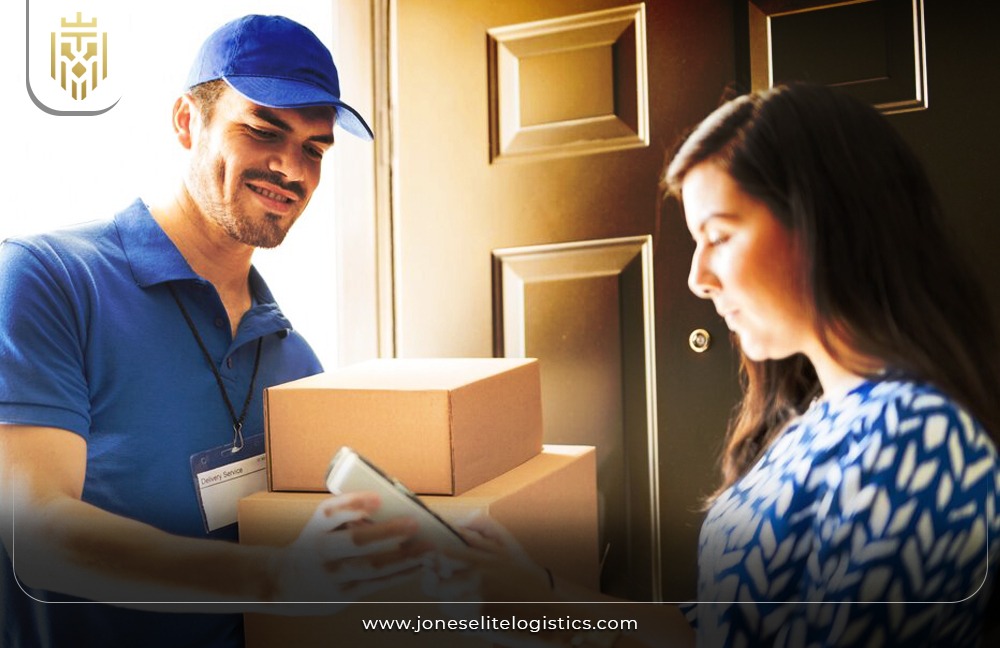

Repairs:
Repair involves the mending of faulty or damaged goods to make them fully operational once again. This reduces the demand for new products, cuts costs, and supports sustainable practices. By extending product life through effective reverse logistics processes, companies can save resources and foster environmental responsibility.

Repackaging:
Repackaging ensures that returned products are in sellable condition. It involves inspecting, cleaning, and re-packaging goods to meet quality standards, reducing shipping costs for those involved in the e-commerce logistics and business and other business sectors.

Recycling:
Recycling focuses on repurposing materials from returned products to create new items. This step reduces the need for raw materials and supports a circular economy, helping companies adhere to sustainability goals. Effective reverse logistics processes ensures the efficient use of resources.
5 Stages of Reverse Logistics:
The reverse logistics process comprises receiving returned products, inspecting them, and deciding on their next steps—whether resale, repair, or proper disposal. This helps companies reclaim value from products through processing returns efficiently while maintaining environmental standards.
Product Returns:
Product returns are initiated by consumers dissatisfied with a purchase. Once a returned item is received, it goes through inspection and documentation. A smooth return process ensures companies handle returns effectively, reducing the costs associated with returned inventory.
Inspection of the Product:
Product inspection is a critical step in evaluating the condition of a returned product. This determines whether the item should be resold, repaired, or disposed of. Efficient inspection ensures accurate processing, leading to reduced waste and improved returns processes.

Processing:
Processing is the next step after inspection, deciding whether a product should be repaired, recycled, or discarded. It ensures a systematic approach to managing returns, allowing companies to handle products effectively based on their condition and reverse logistics costs.
Disposal or Reintegration:
Disposal or reintegration determines the final destination of unsold goods or returned products – whether to dispose of it, recycle it, or return it to the supply chain system. Proper disposal supports sustainability, minimizing environmental impact..
Types of Reverse Logistics:
Reverse logistics is divided into several categories, such as returns management, re-manufacturing, recycling, reuse, and packaging management.
Returns Management:
Returns management focuses on simplifying the returns process for customers. This ensures smoother interactions with clients and minimizes return-related issues. A clear return process and reverse logistics solution lead to higher customer satisfaction.

Remanufacturing and Refurbishment:
Re-manufacturing and refurbishment involve restoring a returned item to its original condition. By reclaiming materials and refurbishing products, companies extend their lifecycle. This process plays a significant role in minimizing waste and returns process costs.
Recycle:
Recycling entails the process of disassembling products virtually to their foundational elements so that they can again be used in manufacturing processes. A well-executed reverse logistics solution supports companies’ efforts to achieve sustainability through effective recycling practices.
Reuse:
Reuse focuses on repurposing returned products without significant modification. This involves selling or donating items that remain valuable to other customers, enhancing resource efficiency and aligning with efficient reverse logistics processes.
Packaging Management:
Packaging management involves recovering and reusing packaging materials. By inspecting and cleaning returned packaging, companies can reduce costs and promote sustainability. This plays a key role in forward logistics as well as overall supply chain efficiency.

Delivery Failure:
Delivery failure occurs when goods cannot be delivered to customers. These products are received back to the warehouse for examination, and this may lead to a process of reposting, resale, or scrapping, which is a crucial part of a company’s return policy and reverse logistics activity.
Unsold Goods:
Unsold goods are returned to manufacturers or distributors for further action. These goods are often liquidated, recycled, or donated. Proper management of unsold goods ensures companies maintain control over inventory and reduce losses from reverse logistics costs.
End Of Life:
End-of-life products are marked by the fact that they have high levels of wear and tear and cannot be used anymore. These items are recycled to extract valuable materials or disposed of via efficient reverse logistics processes.
Benefits of Reverse Logistics:
Reverse logistics offers numerous benefits, including improved brand image, enhanced customer satisfaction, and opportunities for increased revenue.
Improved Brand Image:
Implementing a strong reverse logistics solution enhances a company’s brand image by showing commitment to sustainability. Such a positive brand image may help attract consumers with such preferences and needs as environmentalism and loyalty.
Better Customer Service:
An effective reverse logistics system with a returns process increases customer satisfaction, as products are returned and processed quickly. Returns and exchanges should also be handled effectively and fast since they will also be a key marker to the success of the firm.

Improved Inventory Management:
Reverse logistics helps e-commerce business and other sectors to improve inventory management by providing better visibility into returned items. This allows companies to maintain accurate stock levels and make informed decisions about product reconditioning, resale, or disposal.
Increased Revenue Opportunities:
A strong reverse logistics solution turns returns into revenue opportunities by reselling refurbished items. This not only generates additional income but also helps minimize the financial losses typically associated with returned products.
Product Quality:
Reviewing returned inventory provides valuable feedback on product quality, enabling companies to identify areas for improvement. This feedback helps manufacturers improve on product design and making and therefore lower future product returns

Supply Chain Performance:
Reverse logistics boosts overall supply chain performance by optimizing resource use and reducing waste. It encourages forward logistics strategies that minimize costs while improving operational efficiency and sustainability
Increased Market Penetration:
Refurbished products sold at lower prices help companies reach new market segments. By offering affordable options through optimized reverse logistics, companies increase market penetration and attract cost-conscious customers
Challenges of Reverse Logistics:
Challenges of reverse logistics include high costs, complex return flows, and managing customer expectations. Overcoming these obstacles is crucial for companies to establish efficient reverse logistics processes and maintain profitability.
High Cost:
Managing reverse logistics can be expensive due to labor, transportation, and processing costs. Companies must invest in infrastructure and technology to support their reverse logistics solution while keeping expenses under control.
Customer Expectations:
Consumers want fast and efficient methods to return purchased products. Meeting these expectations requires a well-organized return policy that allows for quick and easy returns.
Environmental Impact:
If not managed properly, returned products can contribute to environmental harm. Organizations have a responsibility to ensure that they do not cause harm to the environment by focusing on recycling, reusing, and proper disposal.

Complex Return Flow:
The process of handling returns is often more complicated than just receiving a returned product. Companies must develop strategies to manage inspection, sorting, and processing returns efficiently to optimize their reverse logistics operations.
Risk of Product Damage:
Returned items are at risk of being damaged during transit or handling. Companies need to implement careful packaging and transportation methods to minimize damage and preserve the value of unsold goods during reverse logistics operations.
How does Jones Elite Logistics help you optimize Reverse Logistics?:
Jones Elite Logistics provides a comprehensive reverse logistics solution as a fulfilment service that helps companies streamline their returns process. They offer return management, fast turnaround times, and detailed analysis of reverse logistics costs, ensuring efficient handling of returns while reducing environmental impact. With their expertise, businesses can effectively manage forward logistics while minimizing costs associated with returns.
FAQs
1) What is Reverse Logistics?
Reverse logistics is the process of returning a product from the end-user or consumer back to the manufacturer or the service provider for re-manufacturing, recycling, or disposal. They concentrate on incorporating the return, so that value can be recovered and waste prevented.
2) What are the benefits of Reverse Logistics?
Some of the advantages are the following: the prospects have a favourable improvement in brand recognition, improved customer relations, efficient stock control, higher revenues, higher product quality, efficient supply chain management, and increased market exposure.
3) What are the challenges of Reverse Logistics?
These include high costs, monitoring customers’ expectations, effects on the environment, intricacies involved in return flows of products, as well as the susceptibility of the products to damage. These factors must be controlled for an efficient reverse logistics system to be realized.
4) What are the 5 R’s of Reverse Logistics?
The 5 R’s are Return, Resale, Repair, Redistribution and Recycling. Both concern themselves with various approaches to dealing with the returned goods as well as ensuring that value is recovered while at the same time cutting down on their environmental footprint.
5) What are the types of Reverse Logistics?
These are returns management, re-manufacturing and refurbishing, recycling and reuse, packaging management, failure in delivery management, responding to excess inventory, and managing end-of-life products.