Supply Chain Management and its Types:
Supply Chain Management (SCM) entails the management and coordination of product movement from the acquisition of raw materials to its delivery to the end users. SCM can be grouped into several types like Agile and Continuous Flow. It minimizes costs, reduces waste, and adapts to market trends. Green SCM integrates environmental practices, ensuring sustainability. Effective supply chain management improves business efficiency and meets customer expectations consistently.

Elements of supply chain management:
Several elements come together to form a supply chain, and they can vary, depending on the industry type, size, and location. They include:

Integration:
Integration in SCM allows for synchrony of supply chain activities, ensuring seamless collaboration among supply chain partners and enhancing supply chain visibility. It leverages supply chain management software to streamline communication and improve supply chain performance by reducing inefficiencies and optimizing responses to demand fluctuations.
Operations:
Operations cover supply chain planning, inventory levels, and distribution processes. Supply chain managers oversee production schedules and quality assurance, ensuring an efficient supply chain that meets market demands. Optimized logistics management guarantees timely deliveries and cost-effective distribution.
Management:
Management in SCM refers to the coordinated activities in terms of planning, organizing, and controlling resources and activities in the supply chain. They implement project management strategies to balance costs and performance. Effective supplier relationships and supply management enhance business resilience and streamline the supply chain process for better outcomes.
Purchasing:
Purchasing in SCM focuses on buying materials and parts required in production and incorporating them into the production process. Supplier management involves negotiations and contract awards to maintain seamless supply chain operations. Strong supply chain strategy improves procurement efficiency and ensures consistency in production.
Distribution:
Distribution includes storage, transportation, and delivery. Advanced logistics provider networks enhance delivery efficiency. Supply chain logistics solutions, like automated warehousing and logistics technologies, optimize transport modes and ensure smooth last-mile delivery, meeting customer expectations.
Innovations:
Technology-driven solutions like IoT, AI, and blockchain enhance supply chain analytics and efficiency. Real-time tracking reduces errors, improves coordination, and strengthens supply chain models by integrating data-driven decision-making.
Seven Principles of Supply Chain Management:
Supply Chain Management (SCM) consists of seven principles that drive the efficient management of logistic chains in businesses. These principles help supply chain managers optimize supply chain activities while meeting customer expectations and ensuring long-term sustainability.
Inventory Visibility:
Visibility of inventory in operations of Supply Chain Management is important so as to track the progress and location of the products across the network. It means a continuous update of the position, location, and condition of stock on the shelves. Greater visibility enables the companies to minimize excess stock holding, experience minimal stock-out situations, as well as facilitate order completion. RFID, IoT, and big data analytics are valuable for the delivery of accurate and timely information on inventory.

Improve Forecasting Models:
The enhancement of Supply Chain Management forecasting models with supply chain analytics improves forecasting accuracy, preventing overproduction or shortages. Supply chain managers use AI-driven supply chain planning to anticipate demand fluctuations and improve the supply chain management process. Effective predictions improve supplier relationships and reduce unnecessary logistics costs.
Enhance Supplier Diversity:
Supplier diversity in Supply Chain Management focuses on increasing SCM firms’ sourcing of diverse suppliers from diverse areas. Supply chain partners from varied regions ensure flexibility in procurement, minimizing dependency on a single source. Supply chain managers promote inclusivity while securing better logistics solutions and improving supply resilience.
Risk Management:
Supply Chain Risk Management deals with the identification of potential risks in the supply chain as well as the control, and treatment of those risks. Chain managers develop contingency plans, ensuring good supply chain management practices reduce vulnerabilities. Effective supply chain strategy integrates alternative sourcing and logistics provider backups to maintain stability
Maintain Partnerships:
Proper management of relationships is crucial in Supply Chain Management to enhance the cooperation between supply chain individuals. Supply chain managers work closely with supply chain partners to foster trust and optimize logistics operations. This ensures supply chain performance remains high through strategic collaboration.
Source Strategically:
In the case of Supply Chain Management, strategic sourcing entails the identification of the best suppliers through an assessment of their functionality, price, and credit standing. Supply chain strategy focuses on operations management by evaluating supply chain models for long-term efficiency. Supply chain managers leverage logistics provider networks to secure competitive advantages.

Sustainability:
Supply chain operations focus on reducing environmental impact through green logistics solutions. Supply chain management work involves adopting eco-friendly supply chain activities such as sustainable packaging, optimized routes, and energy-efficient warehouses. Supply chain managers integrate environmental concerns into strategic decision-making.
Types of Supply Chain Management:
Different supply chain management types cater to various business needs, emphasizing efficiency, speed, or flexibility. Supply chain process selection depends on industry dynamics and customer expectations.
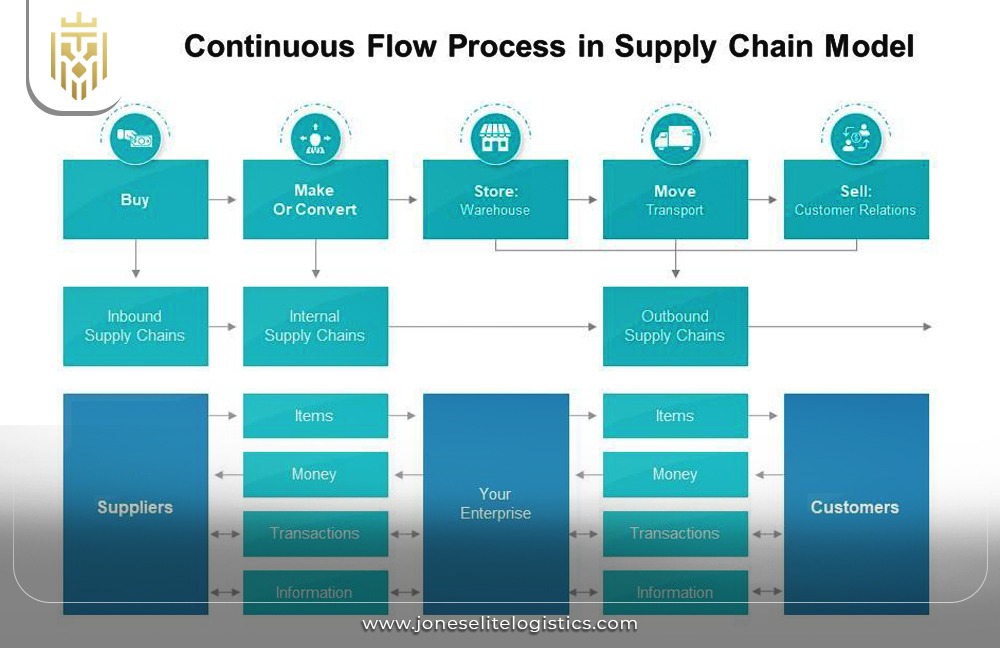
Continuous Flow:
Continuous flow Supply Chain Management is useful for industries that have a constant high need for their products such as the food and beverages industries. Supply chain logistics prioritize logistics management efficiency by minimizing disruptions. Supply chain managers streamline distribution to maintain uninterrupted supply
Agile:
Agile SCM is fit for the environment with high volatilities, fluctuating demand, and a good deal of change as is often seen with products like clothing or electronics. Supply chain managers use real-time data for flexible logistics adjustments. Collaboration with supply chain partners ensures quick response to changes in demand.
Fast Chain:
Fast-chain supply chain management has been useful for industries where the life cycle of products is short such as electronics industries. In the area of organization, the primary consideration is a fast-paced system that applies to everything from the creation of new products to their delivery. This kind of Supply Chain Management is common with companies that focus on fast development and swift entry into the market.
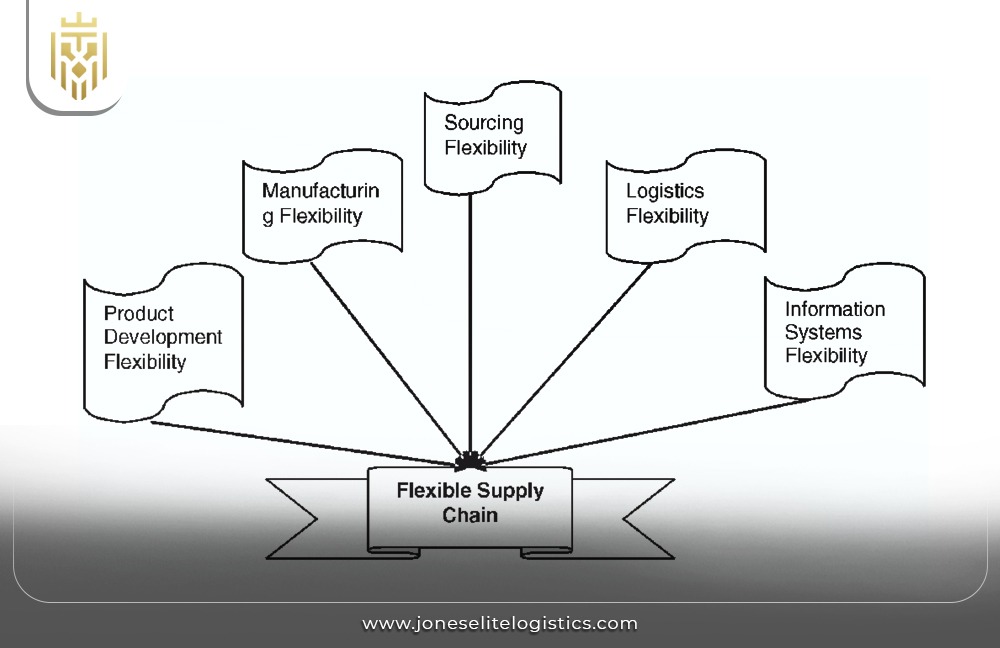
Flexible:
Flexible supply chain operations accommodate seasonal demand fluctuations, such as in agriculture. A supply chain manager adjusts production and logistics dynamically. Supply management ensures cost-effectiveness while maintaining product availability.
Custom Figured:
Industries that need special products or services ranging from automobiles to electronics need custom-configured SCM. The idea hinges on the integration of concepts of both continuous flow and agile Supply Chain Management to afford tailor-made solutions that do not compromise on the flow.
Efficient:
Designed for cost minimization, efficient supply chain management focuses on eliminating waste while maximizing productivity. Logistics networks are optimized through advanced supply chain management software. Chain managers oversee streamlined logistics to maintain low operational costs and high service levels.
Key Considerations while choosing a supply chain type:
Several factors play into choosing the ideal supply chain to prevent potential trouble from coming up. Some of these factors include:
Cost Efficiency:
Cost-effectiveness is one of the primary determinants of deciding on a type of Supply Chain Management. Companies must assess manufacturing costs, inventory levels, transportation expenses, and storage costs. The right supply chain strategy ensures cost reduction while maintaining quality and meeting customer expectations. Supply chain managers must integrate supply chain analytics and supply chain management software for optimal cost control.
Flexibility:
Flexibility is crucial in industries where demand management fluctuates. Companies with adaptable supply chain models can quickly adjust to market shifts. Supply chain planning ensures that businesses can scale operations up or down efficiently, making flexibility a core element of good supply chain management and operational success.
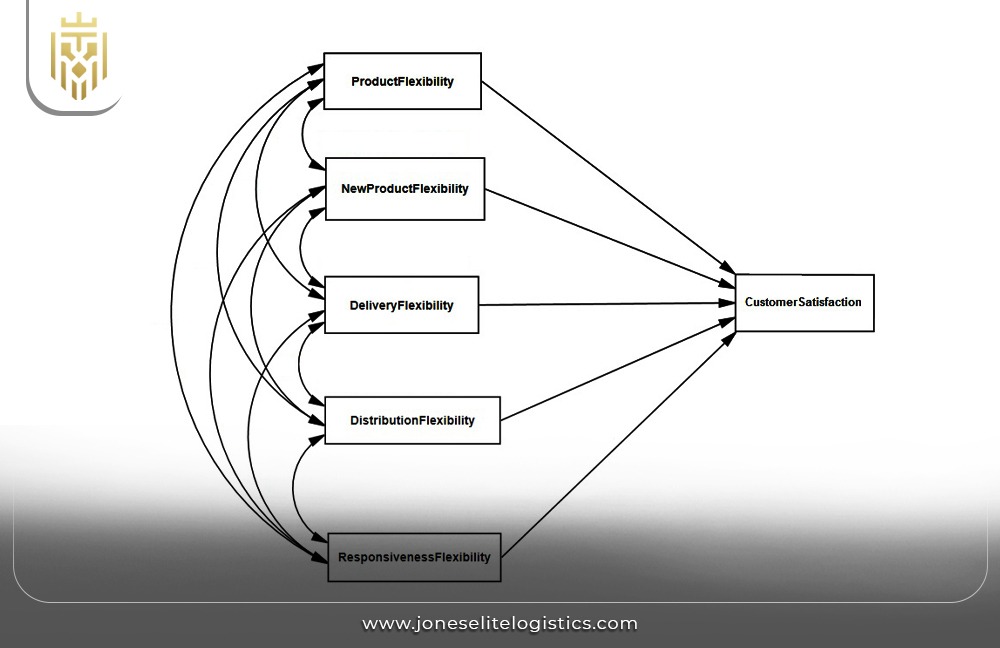
Customer Demand Responsiveness:
Satisfying customer expectations requires an agile supply chain process that aligns with supply chain logistics. Fast and responsive supply chain operations improve service levels. Managers need to assess whether the SCM strategy effectively fits into customer requirements and demand variability.
Importance of Supply Chain Management:
Supply chain management coordinates supply chain activities to optimize goods movement, from suppliers to customers. It enhances supply chain visibility, reduces risks, and ensures an efficient supply chain. Effective supply chain management work results in reduced costs, synchronized production, and minimized waste.
Benefits of Supply Chain Management:
SCM presents many advantages, contributing to the effectiveness of companies and organizations. Strategic supply chain management techniques assist a firm in achieving operational efficiency, which, in turn, results in the improvement of the firm’s performance and efficiency.
Increased Revenue:
Promoting supply chain management can lead to an increase in the company’s revenues since the customer will not experience product unavailability. An effective supply chain manager enhances supply chain performance, improving operational efficiency. Supply chain partners benefit from streamlined processes that minimize costs and maximize sales opportunities.
Improved Quality Control:
Supply management enhances quality by enforcing stringent standards. Strong supplier relationships reduce defects, recalls, and returns, ensuring compliance with industry benchmarks. Supplier management plays a key role in maintaining quality across the entire supply chain.
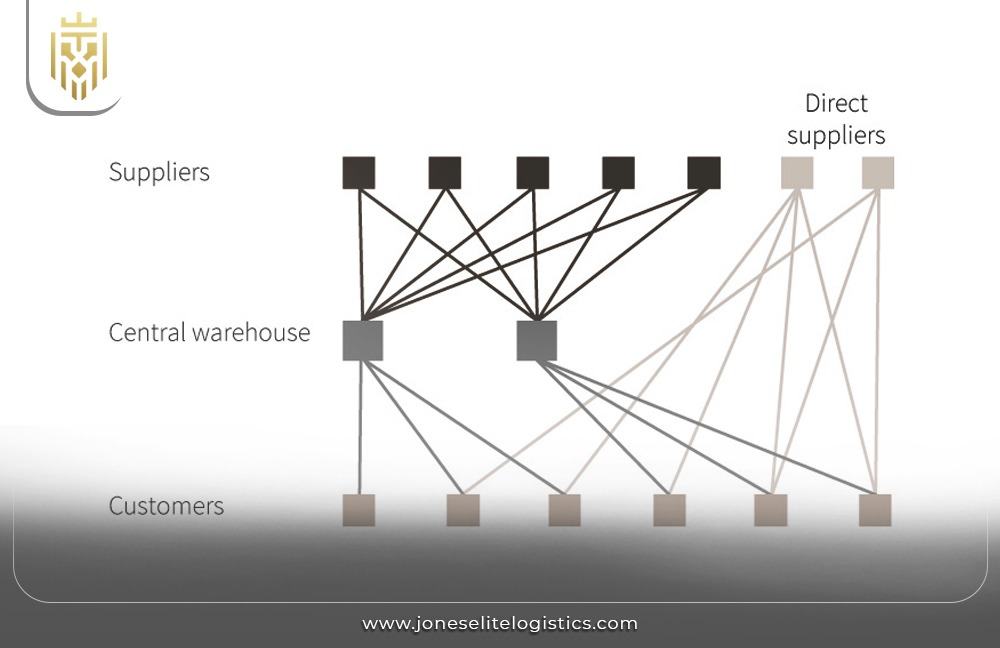
Optimized Distribution:
Efficient Supply Chain Management includes the logic of coordination and planning of the distribution and transportation processes. It helps in the transport of goods from producers to consumers, hence saving them time and costs. This helps in cutting down the lead times and increasing the stock turn which in turn enhances effective distribution networks.
Improved Customer Service:
Enhanced supply chain operations enable faster and more reliable order fulfillment. A supply chain manager oversees operations to improve tracking, accountability, and efficiency. Strong supply chain partnerships contribute to seamless customer interactions.
Shipping Optimization:
Shipping optimization in supply chain management is therefore about the identification of the most appropriate means of shipping. A supply chain manager employs supply chain analytics and supply chain management software to streamline transportation and minimize delays, ensuring smooth delivery processes.
Advancements in Supply Chain Management:
The development of SCM spearheads the breakthroughs and skills applied to technology and consumer needs. As for the currently emerging trends, these are IoT, AI, blockchain, and big data analysis as the principles of supply chain management are increasing. The following advancements act to increase the level of transparency, allow the real-time decision-making process, and also increase efficiency.
FAQs
1) What are the types of supply chain management?
Supply chain management major classifications include continuous flow, agile, fast chain, flexible, custom-configured, and efficient supply chain models, tailored to different market needs.
2) What are the benefits of Supply Chain Management?
Effective supply chain management enhances availability, quality, and cost efficiency while reducing logistics provider expenses and improving supply chain performance.
3) What are the principles of Supply Chain Management?
Key principles involve supply chain strategy, logistics alignment, demand management, collaboration among supply chain partners, and project management for process improvement.
4) What is the importance of Supply Chain Management?
Supply chain management drive efficiency, ensuring optimal supply management, reducing costs, and improving responsiveness, thereby maintaining supplier relationships and sustaining market competitiveness.









